
Cloud Computing refers to the process of making computing services available to users over the internet.
Suppose you own a photography studio; off course you need to find a storage location for all the photos you have. Traditionally you will store those images in Hard disk which will take a lot of physical space, will be expensive and hard to manage. Now what if you use online storages like Google Drive. You can keep all your photos in one place and access them anywhere you want using just your System (Desktop, Laptop, Tablet, Phone) and Internet. That’s Cloud computing for you.
Cloud Services:
- Servers: Servers are data storage and processing devices that provides resources, data, services, or programs to other computers over a network.
- Software: Software is a set of codes or programs that is used to execute specific tasks.
- Databases: A database is an organized collection of structured information, or data, stored in a computer system.
- Networking: Networking refers to process of transporting and exchanging data between different computers or nodes.
- Storage: Storage is a process of saving data to a device.
- Analytics: Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data.
Benefits of Cloud Computing:
- High availability: Services are available whenever and wherever you want.
- Fault tolerance: You can operate freely without the fear of loss of data due to any failures or malfunctions.
- Scalability: You can increase or decrease the services capacity based on your requirement.
- Elasticity: It automatically expands or decrease the processing, memory, and storage resources to meet changing demands.
- Global reach: You can access the services from anywhere in the world.
- Agility: It change quickly and inexpensively to meet your requirements.
Types of Cloud computing:
Public Cloud
Public clouds refers to computing services that are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service providers, which delivers them to users over the Internet.
Features:
- It is owned by cloud services or hosting provider.
- It provides resources and services to multiple users and Organizations.
- It is Accessed via secure network connection (Internet)
- No capital expenditures are required to scale up.
- Applications can be quickly provisioned and deprovisioned.
- Organizations pay only for what they use.
Examples: Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services
Private Cloud
A private cloud refers to cloud computing resources used exclusively by a single business or organization.
Features:
- Organizations create a cloud environment in their datacenter.
- Organization is responsible for operating the services they provide.
- Users outside of the organization cannot access it.
- Hardware must be purchased for start-up and maintenance.
- Organizations have complete control over resources and security.
- Organizations are responsible for hardware maintenance and updates.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid clouds refers to the combination of public and private clouds.
Features:
- Combines Public and Private clouds to allow applications to run in the most appropriate location.
- Provides the most flexibility.
- Organizations determine where to run their applications.
- Organizations control security, compliance, or legal requirements.
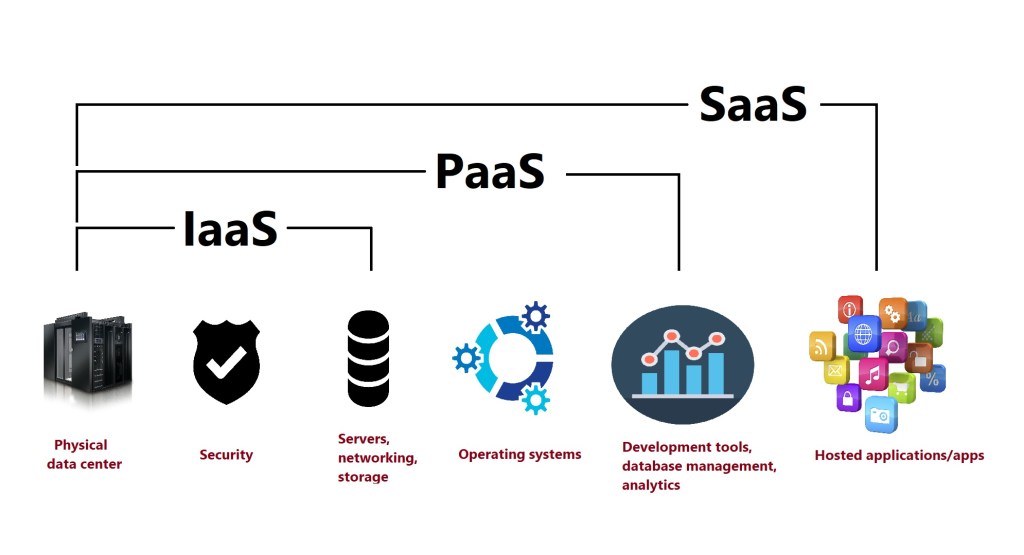
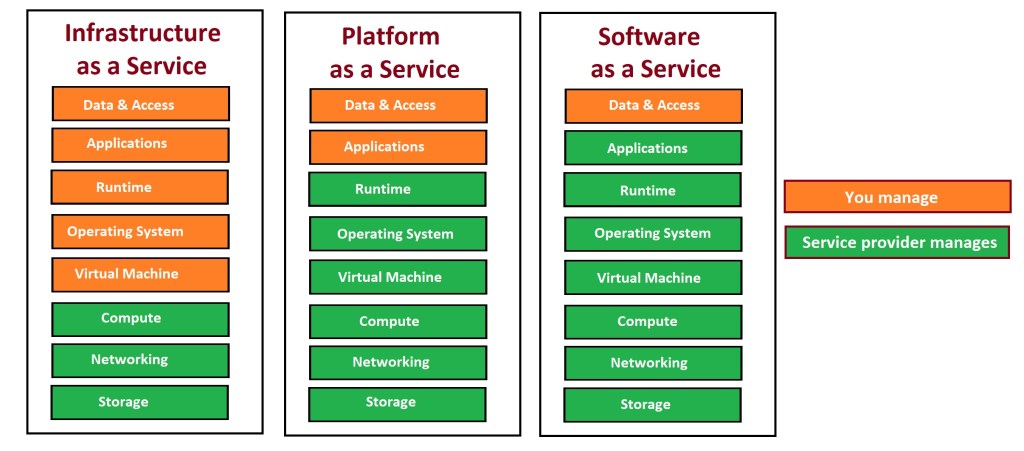
Types of Cloud Services:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is a type of cloud computing service that provides compute, storage, and networking resources to users on demand, and on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is a type of cloud computing service that provides on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications.
Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is a type of cloud computing service that provides software applications over the internet, on demand and on a subscription basis.
Examples: Google Workspace, Dropbox, GoToMeeting.
Thank you for reading and Happy Learning.
Ready to elevate your skills? Click here for my Python book and here for my Machine Learning book on Kindle.
Leave a comment