In a world where data is everywhere but rarely well-understood, data cataloguing is becoming a critical pillar of enterprise data strategy. Whether you’re a data engineer, analyst, or business leader, knowing what data you have, where it lives, and how to trust it is no longer a luxury, it’s a necessity.
So, what exactly is data cataloguing, and how does it work in real organizations?
Let’s break it down.
What is Data Cataloguing?
Data cataloguing is the process of organizing, indexing, and enriching metadata about your organization’s data assets so they are easily discoverable, understandable, and governed.
Think of it as a search engine for your internal data, but with built-in business context, ownership details, quality indicators, and access controls.
How Data Cataloguing Works
1. Data Discovery and Metadata Collection
The process begins by scanning all data sources such as databases, data lakes, cloud storage, APIs, and files to collect technical metadata such as:
- Table names, columns, schemas
- File paths and formats
- Data types, timestamps, and sizes
This gives you a map of what data exists and where it lives.

2. Metadata Enrichment and Business Context
After discovering your data, the catalogue layers in contextual information:
- Business descriptions
- Tags and labels (e.g., PII, sensitive, finance)
- Owners and stewards
- Usage statistics and popularity
- Data quality scores or validation rules
This transforms raw metadata into something searchable and meaningful to technical and non-technical users alike.
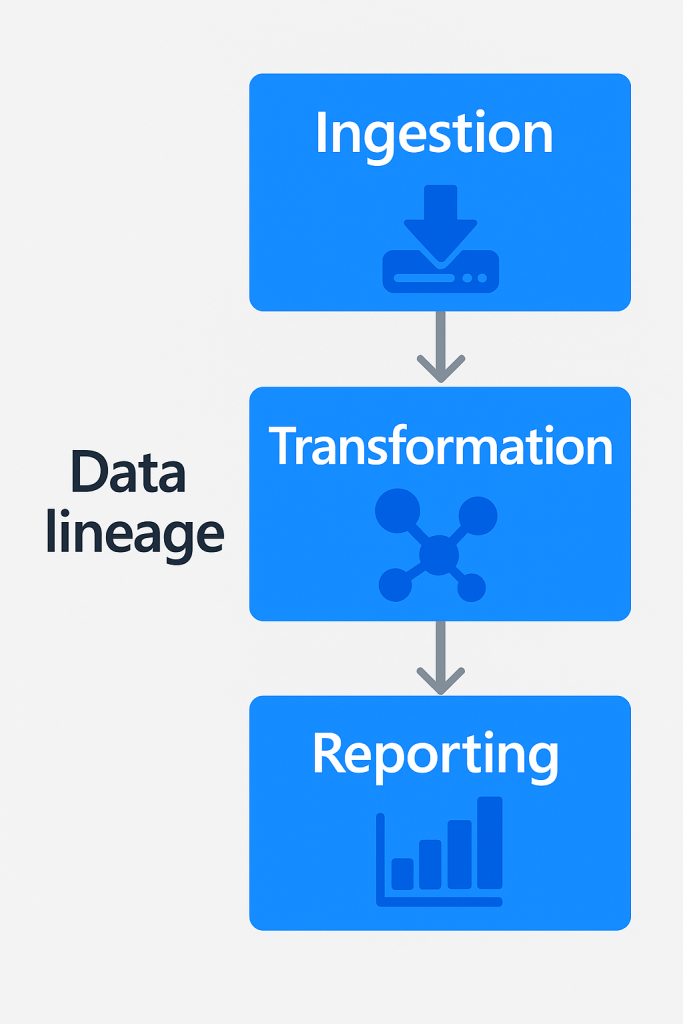
3. Data Lineage Visualization
Lineage tracks how data moves and transforms from origin to destination — for example, from a transactional system → data warehouse → Power BI dashboard.
This is essential for:
- Impact analysis
- Debugging data issues
- Supporting audits and compliance
4. Search and Discovery
With the catalogue populated and enriched, users can now search and explore data assets using a friendly interface:
- “Customer churn table”
- “Sales dashboard data source”
- “Latest inventory updates”
The catalogue surfaces trusted assets, with descriptions, owners, related dashboards, and more which enables faster, smarter decisions.
5. Governance and Access Integration
A good data catalogue is tightly integrated with data governance:
- Role-based access controls (RBAC)
- Data sensitivity classification (e.g., PII, HIPAA)
- Data masking and anonymization policies
- Audit trails for who accessed what and when
This ensures compliance without sacrificing usability.
6. Collaboration and Crowdsourced Knowledge
Modern catalogues allow users to contribute tagging assets, adding notes, upvoting trusted datasets, and sharing best practices.
This social layer helps turn tribal knowledge into shared knowledge breaking down silos across teams.
Why Data Cataloguing Matters
Here’s what effective cataloguing enables:
- Fast, accurate data discovery
- Improved trust and quality
- Stronger data governance and compliance
- Accelerated analytics and innovation
- Empowered self-service for analysts and business users
In short, data cataloguing helps enterprises turn raw data into trusted intelligence.
Popular Data Catalogue Tools
Several powerful platforms lead the space:
- Microsoft Purview
- Alation
- Collibra
- Atlan
- Google Cloud Data Catalog
- DataHub (LinkedIn open-source)
These tools vary in features like automation, AI tagging, lineage, and integration with cloud platforms and BI tools.
Final Thoughts
As enterprises generate more data than ever before, the ability to find, understand, and govern that data becomes a competitive differentiator.
Whether you’re just starting your data governance journey or scaling an enterprise data strategy, a modern, well-integrated data catalogue is one of the smartest investments you can make.
Leave a comment